What is color saturation, and how will it help your images? These questions are the focus of today’s article.
It’s important to know how to use color saturation in your images, whether you’re editing pictures in Lightroom, Photoshop, or any other image editing software. And it’s essential if you’re shooting in RAW, like most photographers.
What is Color Saturation?
You can define saturation as the depth or intensity of color present in an image.
If you’re looking for more vibrant colors in your image, you need to boost your saturation levels. If you reduce saturation, then colors mute and fade.
This doesn’t mean you should overdo saturation in image editing one way or the other. Sometimes, less is more.
How Can You Change Color Saturation?
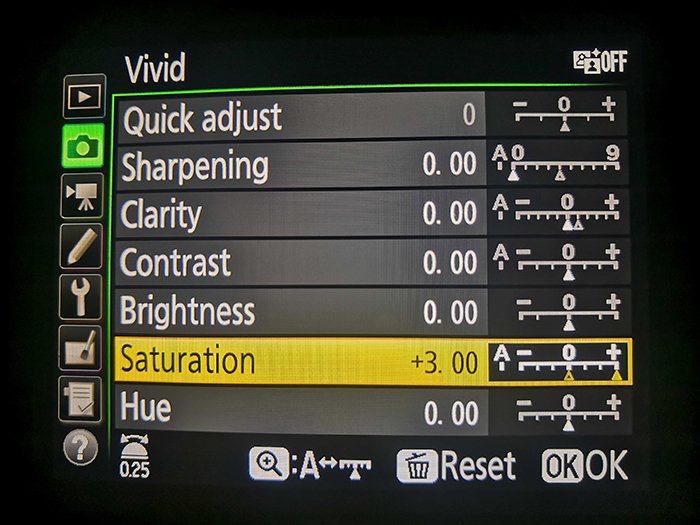
1. In Your Camera Settings
Every camera model is a bit different when it comes to in-camera settings. You can change the saturation in Canon’s Picture Style settings or Nikon’s Picture Control settings. There you’ll find different picture modes like Auto, Portrait, Landscape, Vivid, Monochrome, etc.
If you enter these modes, you can change their default settings. You can control sharpness, clarity, contrast, brightness, saturation, hue, and much more.
2. Using Lens Filters
You can also change color saturation by using certain lens filters, like polarizing filters. These specific filters remove haze from a photo and make the image more saturated and vivid.
3. During Image Editing
In post-production, saturation sliders raise or reduce the intensity of the colors. In this way, you can emphasize or minimize colors even after you have taken the shot.
In Adobe Lightroom, you’ll find this option under the Presence section.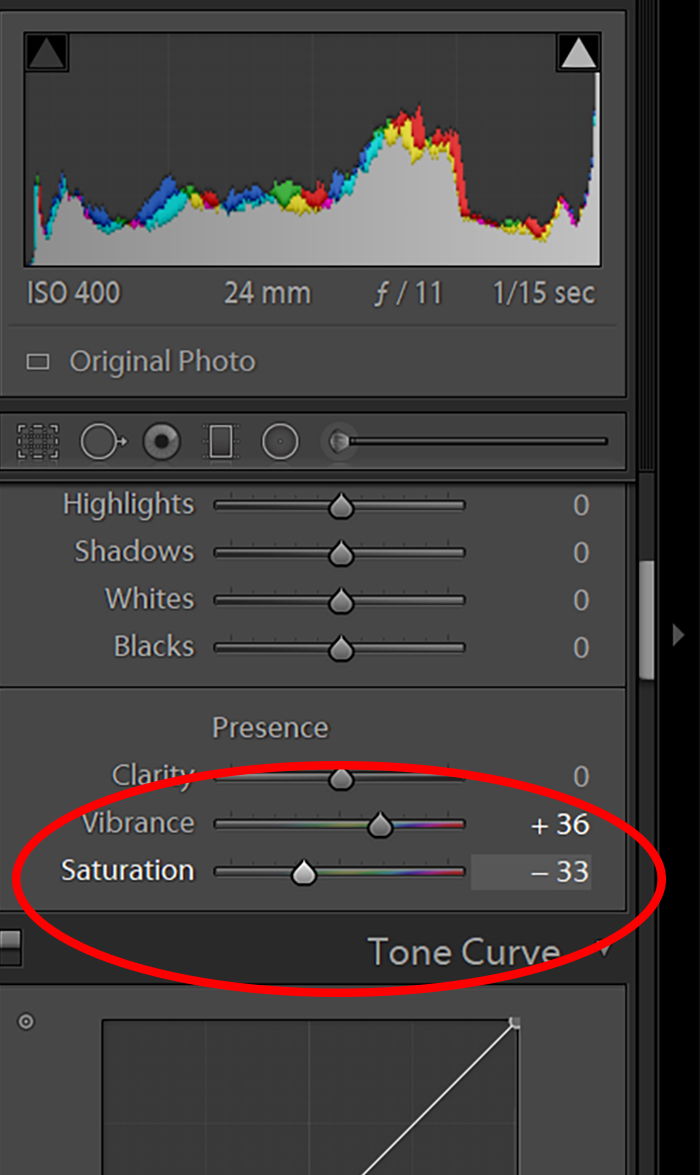
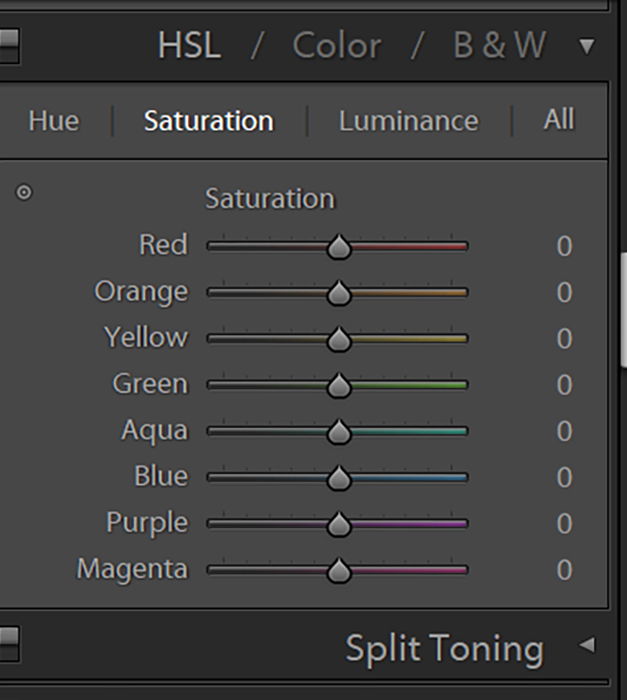
You can also adjust each color’s saturation separately under the HSL panel. Here you can make certain colors weaker or stronger.
The Color Wheel and Color Saturation
When we talk about color saturation in photography, we need to learn a bit about color theory. Color theory is made up of guidelines that explain the visual effects of color. It helps us organize colors into logical structures.
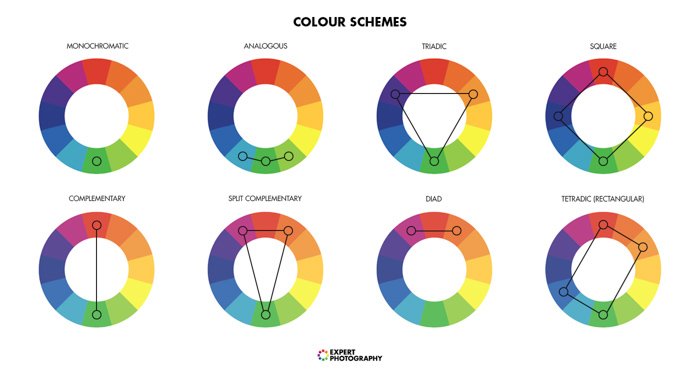
One of the most important aspects of color theory is the color wheel. It’s a circular diagram representing the appealing relationships between.
We can learn about different color combinations from the color wheel, like complementary colors, monochromatic colors, analogous colors, etc.
Complementary colors have the strongest contrasts that result in energetic combinations. Therefore, these pairings are most striking at maximum saturation. But if you want to lessen the effect of their contrast in your image, you should decrease the saturation of these colors.
Color Space and Color Saturation
Color space is another term we need to understand when learning about saturation in photography. Color space refers to the color range that a photo can showcase. It’s like a digital color palette.
The most common choices of colors space are sRGB and Adobe RGB.
RGB refers to red-green-blue, the primary colors from which all colors are created. It’s recommended that you use RGB color space in digital photography. It reproduces a broader spectrum of color saturations.
The standard color model used in computer screens and other digital devices (tablets and smartphones) is sRGB. It reproduces only 75% of the color that Adobe RGB does.
RGB shows color closer to what the human eye can take in. This is why you want to modify colors in this color mode when you’re editing a digital photo. You’ll have more accurate colors if you choose to print them.
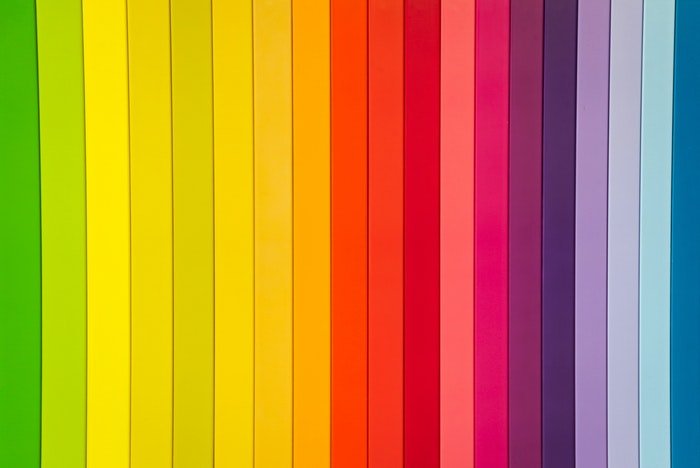

How Can Color Saturation Improve Your Photos?
Changing color saturation can create a certain mood in an image or enhance certain feelings of your viewer.
You can raise color saturation to boost the overall intensity of your image. More saturated images can portray a happier mood and illustrate passionate feelings.
However, if you oversaturate the image, your viewers may be put off by it. Very intense colors can sometimes look unrealistic or gaudy. You need to know when enough is enough.
On the other hand, if you find your images a little too intense, you can reduce the saturation. You can desaturate an image to create a minimalist effect and a more somber and subdued mood.
Many photographers also find it best to change color saturation only in selected areas through masking. That way, they have much more creative control over what areas they want to be affected.

Conclusion
Color saturation can enhance your photos to make images look more or less saturated if you use it well. You can change color saturation through your in-camera settings, with filters, or in image editing software.
By learning more about color theory and color space, you can train your eyes to use color saturation better. You’ll be able to use it to enhance your image’s mood and quality.
Do you want to improve your photo editing skills? Take our Effortless Editing with Lightroom course to edit your images quickly and beautifully.

